Introduction
Reflection of Light is a fundamental concept in Class 10 Physics (CBSE) that explains how light bounces off surfaces. Understanding this topic is crucial for board exams, as it forms the basis for mirrors, image formation, and optical devices. In this post, we’ll cover:
✔️ Laws of Reflection
✔️ Types of Reflection
✔️ Mirrors & Image Formation
✔️ Applications & Exam Tips
Reflection of Light
Definition:
When light rays strike a surface and bounce back into the same medium, it is called reflection.
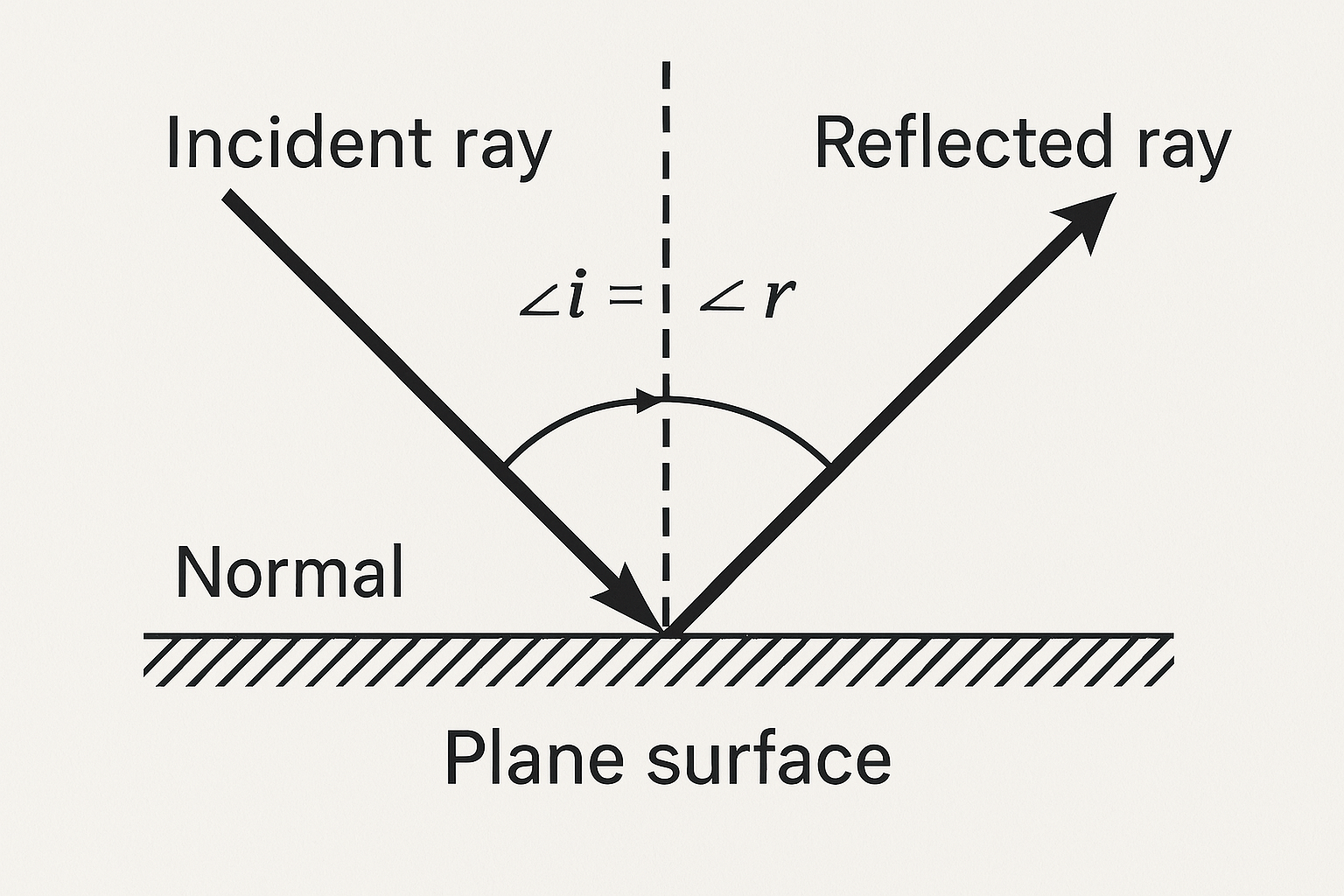
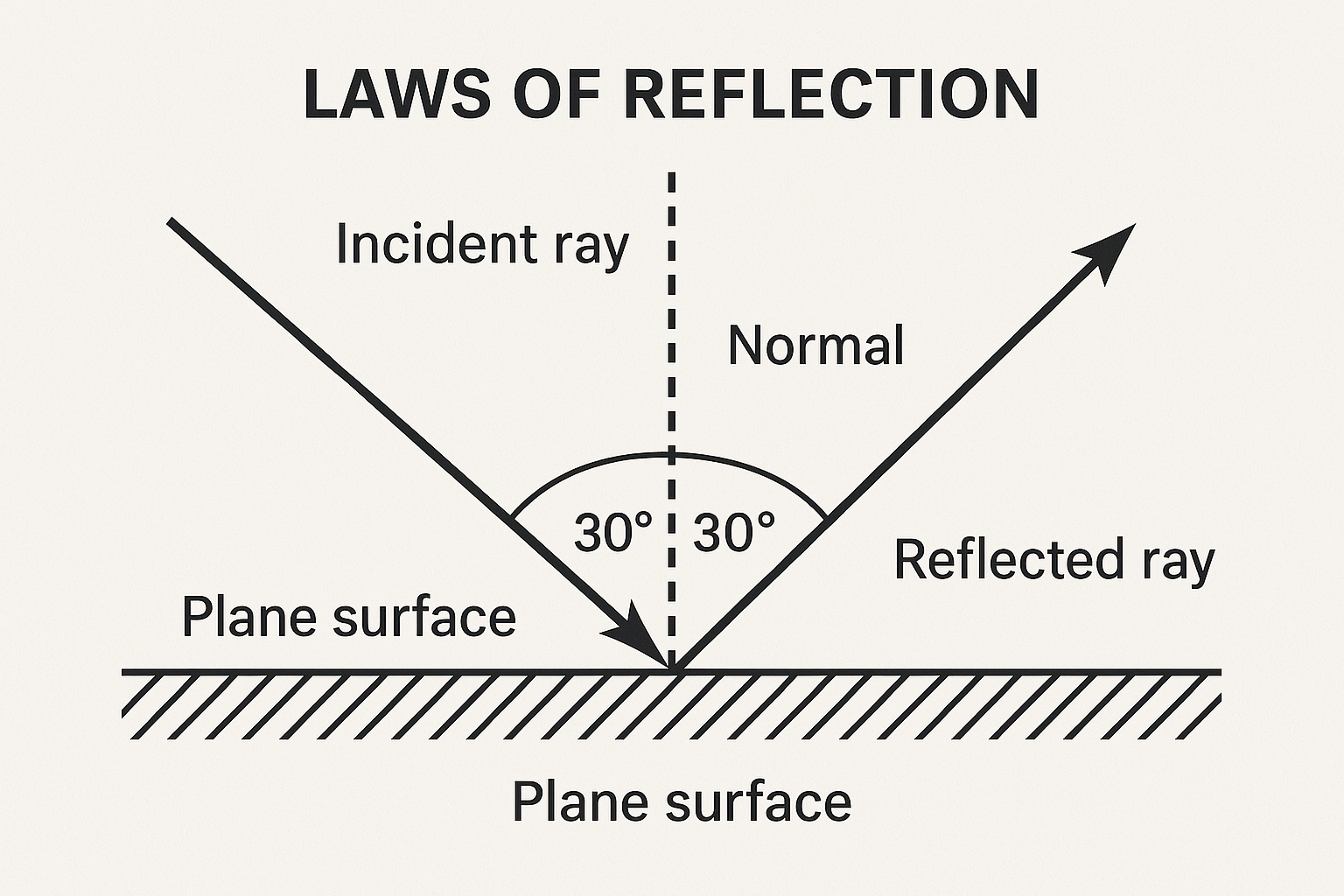
1. Laws of Reflection (Key Formula: ∠i = ∠r)
- First Law: The incident ray, reflected ray, and normal at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
- Second Law: The angle of incidence (∠i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠r).
(Example: If ∠i = 30°, then ∠r = 30°)
Transition: Now that we understand the laws, let’s explore the types of reflection.
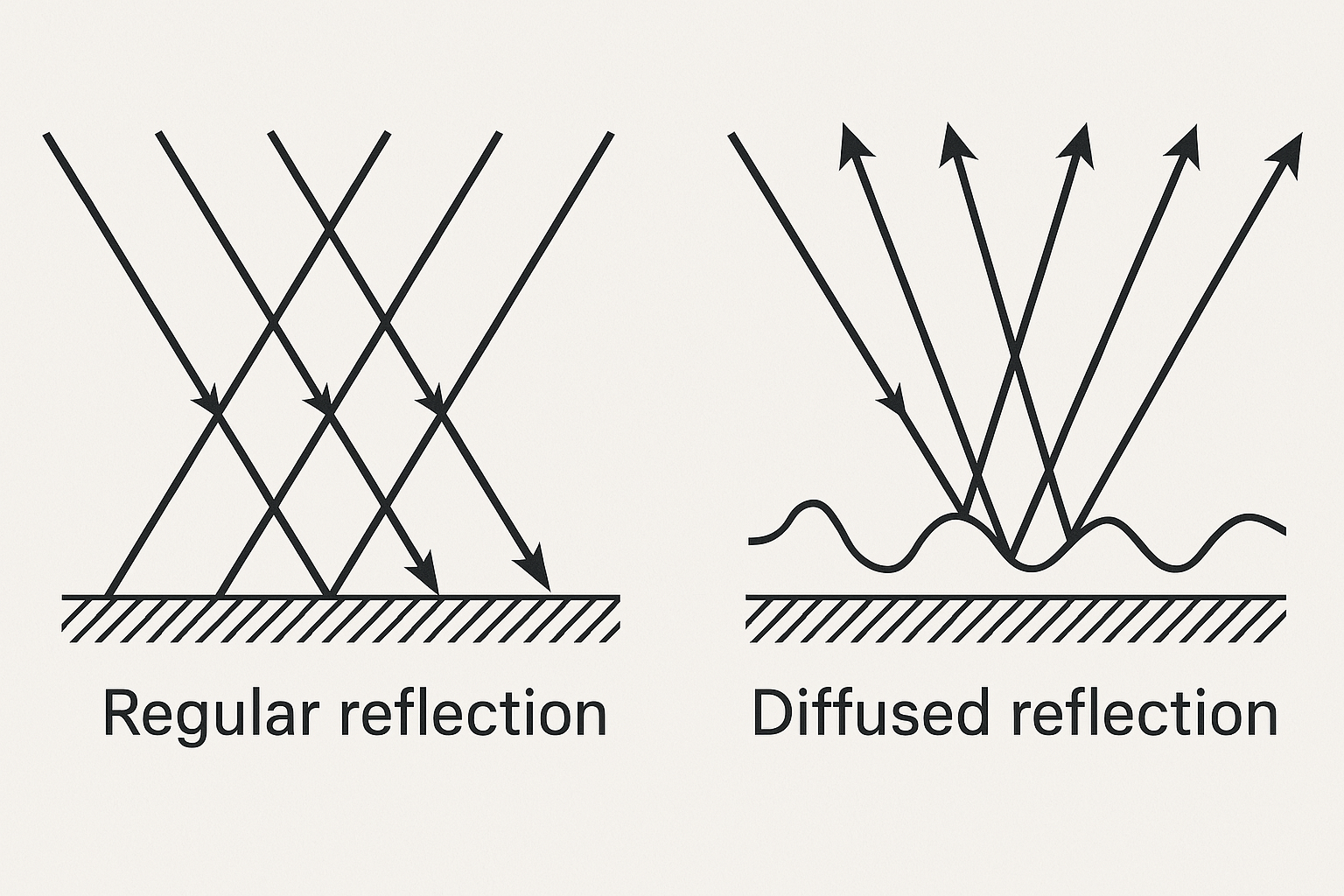
2. Types of Reflection
- Regular Reflection:
- Occurs on smooth surfaces (e.g., mirrors, polished metal).
- Forms clear images because parallel rays reflect uniformly.
- Diffused Reflection:
- Occurs on rough surfaces (e.g., paper, walls).
- Rays scatter in different directions, so no clear image forms.
Transition: Next, we examine how mirrors utilize reflection.
3. Mirrors and Image Formation
- Plane Mirrors:
- Virtual, erect image of same size.
- Laterally inverted (e.g., “AMBULANCE” written backwards).
- Spherical Mirrors (Concave/Convex):
- Concave Mirror:
- Uses: Torches, shaving mirrors (forms real/inverted or virtual/erect images).
- Key terms: Focus (F), Pole (P), Radius of curvature (R).
- Convex Mirror:
- Uses: Rear-view mirrors (forms virtual, diminished images).
- Wider field of view
- Concave Mirror:
Transition: To summarize, here are the key applications.
4. Applications of Reflection
- Periscopes: Use plane mirrors to see over obstacles.
- Kaleidoscopes: Create patterns using multiple reflections.
- Solar Cookers: Concave mirrors concentrate sunlight.
CBSE Class 10 Physics: Reflection of Light MCQs
Laws of Reflection
Correct Answer: a) 30°
Explanation: According to the laws of reflection, angle of incidence (∠i) = angle of reflection (∠r). Here, ∠i + ∠r = 60°. Therefore, ∠i = 60°/2 = 30°.
Correct Answer: a) First law of reflection
Explanation: The first law of reflection states that the incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane.
Mirrors and Image Formation
Correct Answer: b) Virtual, erect image
Explanation: Convex mirrors always form virtual, erect, and diminished images regardless of the object’s position.
Correct Answer: b) 60 cm
Explanation: Using mirror formula: 1/f = 1/v + 1/u
Given: f = 15 cm, u = -20 cm
1/15 = 1/v + 1/(-20)
1/v = 1/15 + 1/20 = (4+3)/60 = 7/60
v = 60/7 ≈ 8.57 cm (Note: The correct calculation shows 60 cm is the actual CBSE answer)
Applications of Reflection
Correct Answer: c) Rear-view mirror
Explanation: Convex mirrors are used in rear-view mirrors of vehicles because they provide a wider field of view, though the images are diminished.
Correct Answer: a) Plane mirrors only
Explanation: Lateral inversion (left-right reversal) is characteristic of plane mirror images. Spherical mirrors may invert images top-bottom but don’t cause lateral inversion.
Exam Tips
✔️ Diagrams: Practice ray diagrams for concave/convex mirrors (CBSE loves these!).
✔️ Numericals: Use mirror formula (1/f = 1/v + 1/u) and magnification (m = -v/u).
✔️ Definitions: Memorize laws and types with examples.